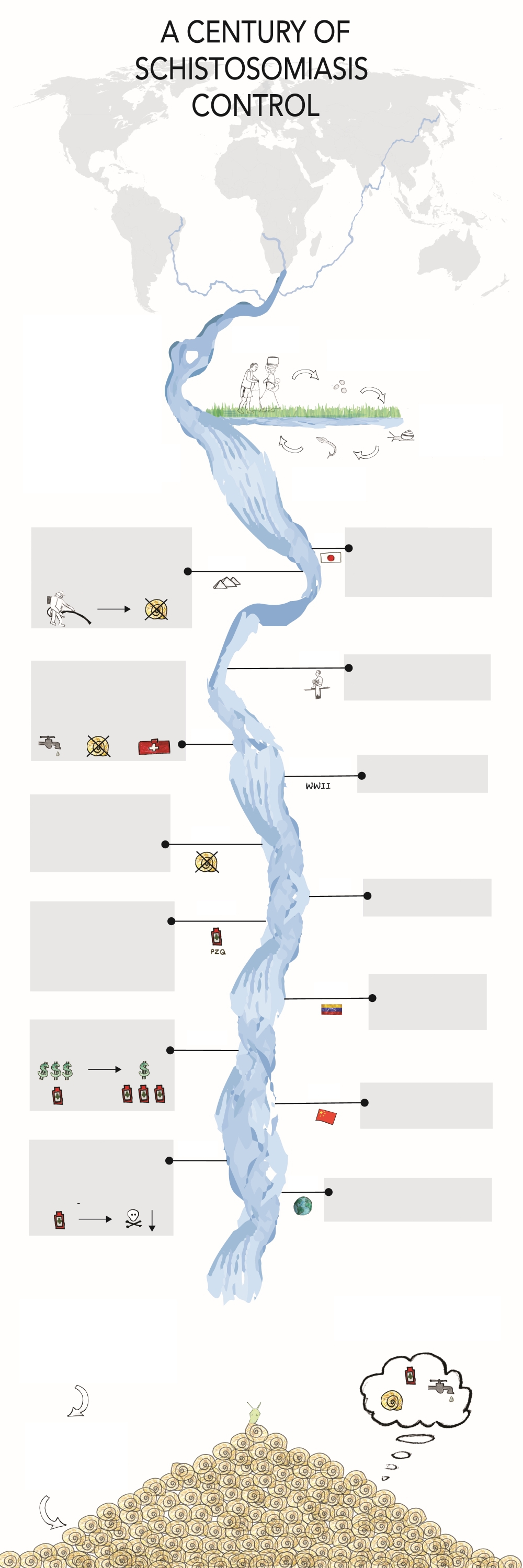
WHAT?
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease infecting more than
250 million people worldwide today, with nearly
800 million at risk. Chronic infection leads to anemia, growth stunting, cognitive impairment, fatigue, infertility, and in some cases, liver fibrosis or bladder cancer.
Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease infecting more than
250 million people worldwide today, with nearly
800 million at risk. Chronic infection leads to anemia, growth stunting, cognitive impairment, fatigue, infertility, and in some cases, liver fibrosis or bladder cancer.
Cercariae infect people in contact with fresh water
Infected people contaminate fresh water with urine or feces containing schistosome eggs
In the water, miracidia hatch from eggs and contaminate snails
Snails release a large number of cercariae into the water
1904
The government of Japan devises the first national schistosomiasis control strategy, focused on an integrated approach of treating patients and controlling snails and parasite eggs in the environment.
1920's
Egypt is one of the first countries to implement the use of drugs and molluscicides in an effort to control schistosomiasis. Chemical snail control efforts using copper sulfate gain recognition with successful reduction.
1930's
Control efforts in Egypt shift toward borehole latrines as a sanitary measure against schistosomiasis, without much success.
1940's
Control strategy recommendations by the World Health Organization promote the importance of integrated control measures, emphasizing access to clean water, sanitation, snail control, health education, and health services, in addition to drug treatments.
1939-1944
World War II notably stalls Japan’s successful reductions of schistosomiasis prevalence.
1950's
China, Puerto Rico and Venezuela begin national schistosomiasis control programs focused primarily on control of snails. Many other countries follow suit in the next few decades.
1980
Japan, Lebanon and Tunisia eliminate schistosomiasis by using snail control primarily!
1980's
Praziquantel, an anti-parasitic drug, becomes the drug-of-choice for treating schistosomiasisas after being introduced and proven effective. The integrated approach is supplanted by chemotherapy via mass drug administration (MDA).
1984
Venezuela achieves a 94% reduction in schistosomiasis since baseline, with a program focused primarily on snails.
1990's
MDA approach increases as a generic less expensive form of Praziquantel becomes available.
1995
China introduces praziquantel into their integrated control program and achieves further schistosomiasis reductions.
2000's
Preventive chemotherapy, using Praziquantel, is officially endorsed as the primary strategy for global schistosomiasis control with the goal of reducing morbidity associated with high worm burdens.
2015
By our estimates, 68 countries remain endemic for schistosomiasis, 52 suffer from moderate to high schistosomiasis transmission according to the WHO.
TODAY
Use of mass drug treatment in hightransmission areas at whatever level of coverage is manageable. In lowtransmission areas, the recommended focus is on transmission reduction.
Use of mass drug treatment in hightransmission areas at whatever level of coverage is manageable. In lowtransmission areas, the recommended focus is on transmission reduction.
RESULT
Re-infections in hightransmission areas due to large numbers of snails in fresh water sources.
Re-infections in hightransmission areas due to large numbers of snails in fresh water sources.
WHAT’S NEXT?
